The theory of relativity
The principle of relativity states that the laws of physics are the same for all observers in uniform motion relative to one another. This means that there is no preferred frame of reference in the universe, and that all motion must be relative to some other object or observer.
The second postulate of the theory of relativity is that the speed of light is always the same, regardless of the motion of the observer or the source of the light. This is known as the constancy of the speed of light, and it has been confirmed by numerous experiments.
Special relativity deals with the behavior of objects moving at high speeds relative to one another. It proposes that the laws of physics are the same for all observers moving at a constant velocity relative to one another. In addition, special relativity predicts that time and space are not absolute, but are relative to the observer and the motion of the objects being observed. This means that time can appear to pass differently for different observers, depending on their relative motion. For example, a clock moving at high speed relative to an observer on Earth will appear to run slower than an identical clock at rest on Earth.
The theory of general relativity deals with the effects of gravity on the structure of space and time. It proposes that gravity is not a force, but rather the result of the curvature of spacetime caused by the presence of mass and energy. This means that objects with mass create a "gravity well" in the fabric of spacetime, which causes other objects to move towards them. General relativity also predicts the existence of black holes, which are regions of spacetime where the gravitational pull is so strong that nothing, not even light, can escape.
The theory of relativity is summarized by Einstein's famous equation, E=mc², which relates energy (E) to mass (m) and the speed of light (c). This equation shows that a small amount of mass can be converted into a large amount of energy, as demonstrated by nuclear reactions. The equation has had important implications for nuclear physics and energy production.
Overall, the theory of relativity has had a profound impact on our understanding of the universe and has been confirmed by numerous experiments and observations. It remains one of the most important theories in modern physics.
Modern invention in theory of relativity
Research on the theory of relativity is an ongoing field of study, with many new discoveries and developments being made in recent years. Here are a few examples of modern research on the theory of relativity:
Gravitational waves: In 2015, the Laser Interferometer Gravitational-Wave Observatory (LIGO) detected gravitational waves for the first time, providing direct evidence for Einstein's theory of general relativity. Since then, numerous other detections have been made, opening up a new field of astronomy that allows scientists to study the most extreme events in the universe, such as the collisions of black holes and neutron stars.
Black holes: The theory of general relativity predicts the existence of black holes, but many of their properties remain mysterious. Recent research has focused on studying the behavior of matter and radiation around black holes, as well as attempting to resolve some of the paradoxes associated with them, such as the information loss problem.
Cosmology: The theory of general relativity is also used to study the large-scale structure and evolution of the universe. Recent research has focused on developing new models of the universe that incorporate dark matter and dark energy, which are thought to make up the majority of the universe's mass and energy.
Tests of relativity: Despite the success of the theory of relativity, there are still some unresolved questions and areas of uncertainty. Researchers are continually testing the theory through a variety of experiments, including precision tests of the gravitational constant, measurements of the properties of the cosmic microwave background radiation, and observations of the orbits of stars around supermassive black holes.
Overall, research on the theory of relativity is a thriving field that continues to advance our understanding of the universe and its fundamental laws.
-Source- ChatGPT
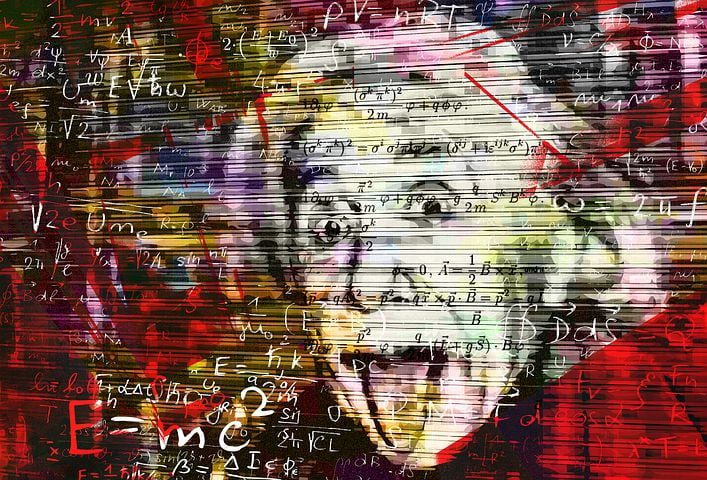










No comments:
Post a Comment